In partnership with Kennesaw State University’s Department of Museums, Archives & Rare Books, the Digital Library of Georgia has just added a collection of oversized technical drawings from the Gregson and Ellis Architectural Drawings Collection that document the experiences of “living and receiving medical and mental health care in the mid-20th century segregated South,” according to Helen Thomas, the outreach archivist at Kennesaw State University Archives.
The collection, available at https://dlg.usg.edu/collection/gkj_gead, features facilities located across Baldwin, Richmond, Treutlen, Ware, and Wayne counties in Georgia. The digitized drawings will also be made available through KSU’s Scholarly Online Access Repository (SOAR) at https://soar.kennesaw.edu/handle/11360/5132.
Some images from the collection include:
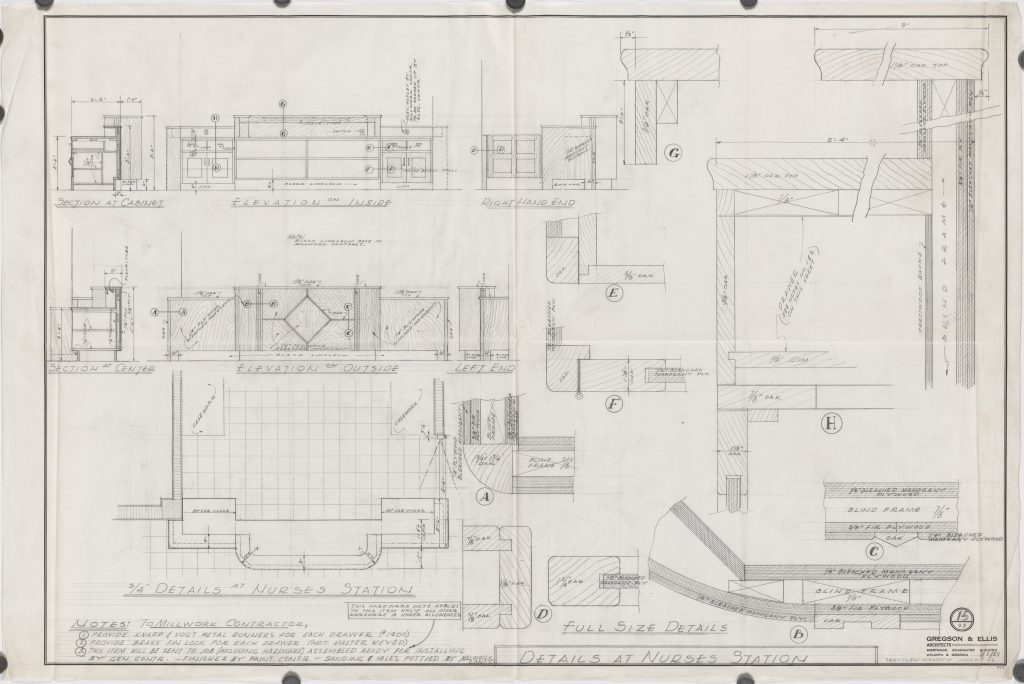
Collection: Gregson and Ellis Architectural Drawings
https://dlg.usg.edu/record/gkj_gead_treutlen-020
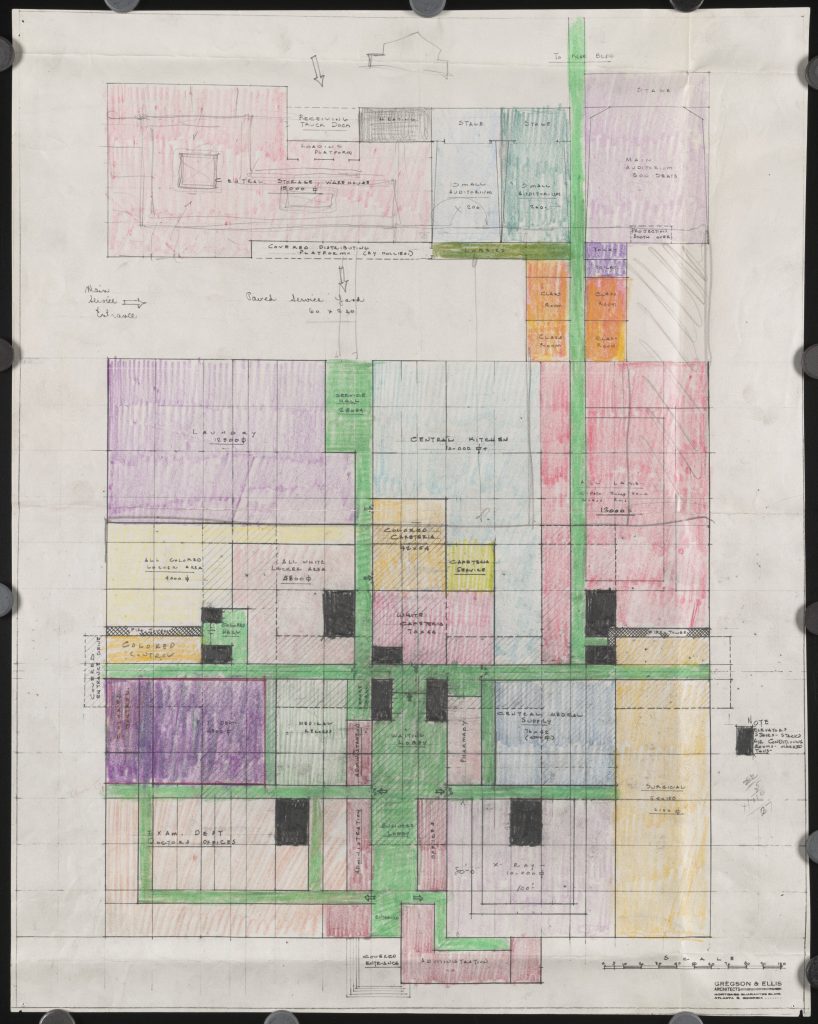
Collection: Gregson and Ellis Architectural Drawings
https://dlg.usg.edu/record/gkj_gead_augusta-005
Thomas, who works regularly with these materials, adds: “Architectural records demonstrate not only trends in construction and design, but also reflect the society in which the buildings exist…The materials we proposed to digitize depict public facilities, from small rural hospitals to large medical complexes, representing the medical services available to all Georgians regardless of their level of income.”
She concludes: “Since each set of drawings shows public facilities built in Georgia before the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, these drawings demonstrate how buildings were constructed to segregate not only by the facility but also within facilities. While some of the drawings in this collection reveal separate buildings constructed for the same purpose, but each restricted to white or African-American citizens (such as separate psychiatric buildings in the Milledgeville complex for white and African-American patients), some show how individual buildings were segregated. An example of the latter is the Augusta State Hospital, which shows separate entrances, waiting areas, restrooms, cafeterias, pharmacies, pediatric wings, and locker rooms for white and African-American patients and employees.”
Barbara Berney, Ph.D., MPH, used the Gregson and Ellis materials in her documentary Power to Heal: Medicare and the Civil Rights Revolution, and says:
“This documentary examines the history of inequality in Americans’ access to health care, and specifically how Medicare was used to desegregate thousands of hospitals across the country. As a scholar of public health and the U. S. health care system, I was inspired to produce the film by hearing eyewitness accounts from physicians, nurses, and government staffers involved in the integration effort and those who struggled to provide health services in rural areas lacking the most basic medical care. The Gregson and Ellis collection provided context for these firsthand accounts by illustrating the physical space in which these health care professionals were working…In addition to providing multiple examples of public hospitals of this era, these drawings show that the public medical facilities available to African Americans were not only separate but could also be limited in size and capabilities.”
About the Kennesaw State University Archives
The Kennesaw State University Archives is a destination for university and community members to research the history of Kennesaw State University and people and organizations in north and northwest Georgia. The mission of the KSU Archives is to identify, collect and make accessible records of enduring value to preserve institutional and community memory into the future. For more information, visit archives.kennesaw.edu.

