A premier online compilation of digital civil rights content is relaunching with a new look and thousands of additional pieces of history.
The milestone marks a new era for the Civil Rights Digital Library (CRDL). This project brings together more than 200 libraries, archives, and museums to provide free online access to historical materials documenting the Civil Rights Movement in the United States. These collaborative partnerships are the bedrock of this national project.
View the entire collection online at https://crdl.usg.edu/.
Barbara McCaskill, an English professor at the University of Georgia who serves as director of the Civil Rights Digital Library and other projects, notes:
“Since its launch in 2008, the Civil Rights Digital Library has played a meaningful role in advancing the understanding of America’s civil rights activism at a time when upticks in racially motivated violence and crime and the erosion of voting rights have attached more urgency than ever to issues of equality, equity, human dignity, and freedom.”
She says:
“The signal achievement of this resource is its varied and unique content about people, places, and events. But it also challenges users to expand their knowledge of civil rights studies beyond national icons such as Dr. King and Rosa Parks, cities such as Atlanta and Birmingham, and beyond the 50s, 60s, and 70s to the present day.“
”As a result, the Civil Rights Digital Library continues to demonstrate a transformative impact on scholarship and instruction, as well as on how we carry ourselves as citizens and come together in community.”
First funded by a National Leadership Grant from the Institute of Museum and Library Services, the Civil Rights Digital Library launched in 2008 as part of the University System of Georgia’s GALILEO statewide virtual library initiative. Along with these continuing collaborations, the Digital Library of Georgia , an initiative of GALILEO and the University of Georgia Libraries, administers the site.
In addition, support continues to be provided by the following partners:
- Georgia Humanities,
- the Walter J. Brown Media Archives and Peabody Awards Collection,
- the New Georgia Encyclopedia,
- and the Franklin College of Arts & Sciences, University of Georgia.
Since 2005, the portal has grown from about 100 collections to more than 350 collections of digitized content, including primary sources and educational resources.
The Civil Rights Digital Library contains contributions from statewide and national partners, documenting the civil rights era, including:
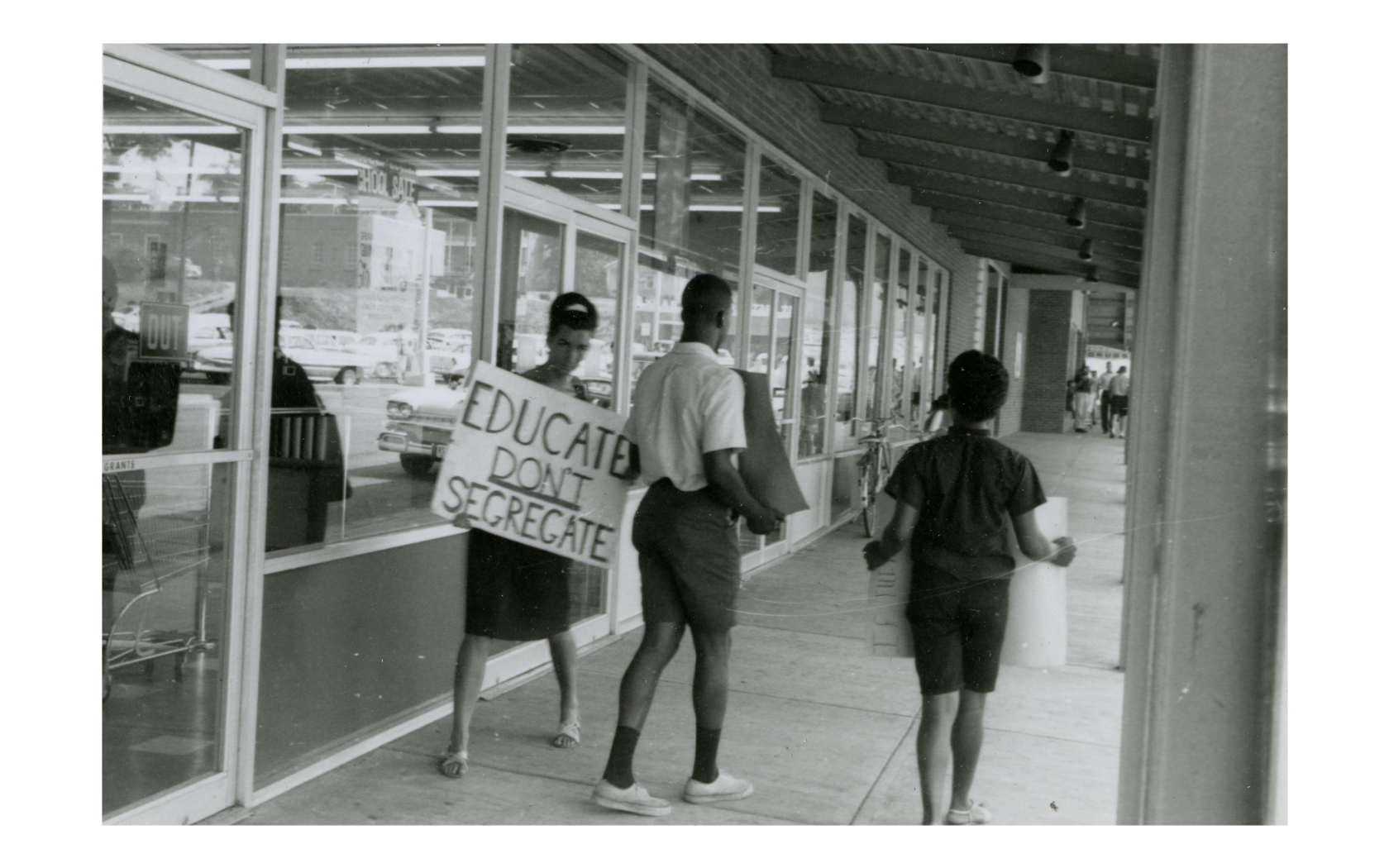
- The desegregation of Central High School in Little Rock, Arkansas (1957).
- The Atlanta Temple bombing (1958),
- The Atlanta sit-ins (1960),
- The Freedom Rides (1961),
- The desegregation of the University of Georgia and Georgia Tech (1961),
- The Albany Movement (1961–1962),
- The desegregation of the University of Mississippi (1962), Clemson University (1962), and the University of Alabama (1963),
- The Birmingham Demonstrations (1963),
- The Americus Movement (1963, 1965).
Researchers and visitors can search the content of the Civil Rights Digital Library in numerous ways, including geographic location browsing with an interactive map that identifies civil rights movement-related resources in all 50 states.
The site also contains:
- Biographical information for more than 3,000 people active during the civil rights era, which can be browsed alphabetically by surname. Many of these civil rights workers and foot soldiers may not be familiar, but their commitment to the movement formed the backbone of transformative civil rights campaigns and social reform.
- New Georgia Encyclopedia (NGE) articles that cover events and individuals associated with the civil rights movement in Georgia. In addition to the concise, authoritative articles, images, multimedia files, and online exhibitions in the NGE further investigate civil rights figures and events. NGE’s content is made possible by Georgia Humanities in partnership with the University of Georgia Press, the University System of Georgia/ GALILEO, the University of Georgia Libraries, and the Office of the Governor.
- Raw newsfilm footage from Georgia television stations WSB (Atlanta) and WALB (Albany) preserved through the University of Georgia Libraries’ Walter J. Brown Media Archives and Peabody Awards Collection. These stations covered civil rights events throughout the entire southeastern United States.
- Exhibits drawn from materials belonging to partner libraries, archives, and museums across Georgia, created by Georgia graduate students in collaboration with the DLG and NGE.
“By relaunching an expanded site on Sept. 9, 2022, the 65th anniversary of the 1957 Civil Rights Act, the Digital Library of Georgia celebrates the first federal civil rights legislation of the 20th century,” adds Sheila McAlister, director of the Digital Library of Georgia. “The relaunch demonstrates the DLG’s commitment to reflecting and sharing the diversity of experiences in Georgia and nationwide.”
View the entire collection online at crdl.usg.edu
Download the Civil Rights Digital Library 2022 Press Kit here.
Selected images:

Series of WSB-TV newsfilm clips of a civil rights march and resulting arrest; civil rights preachers and local officials speaking at mass meetings; groups of Albany city officials as well as civil rights leaders entering the federal courthouse; and Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., and Reverend Ralph D. Abernathy at a press conference in Albany, Georgia, 1962 July. In this still image, Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. expresses his disappointment of the injunction blocking demonstrations issued by federal district judge J. Robert Elliott and his gratitude for the reversal of that injunction by Judge Tuttle. He calls the audience to present their bodies as a significant witness by continuing to move and work for freedom. Courtesy of the Walter J. Brown Media Archives and Peabody Awards Collection.

Series of WSB-TV newsfilm clips of African American civil rights workers, Georgia National Guardsmen, and city officials in Albany, Georgia, 1961 December. Courtesy of the Walter J. Brown Media Archives and Peabody Awards Collection.
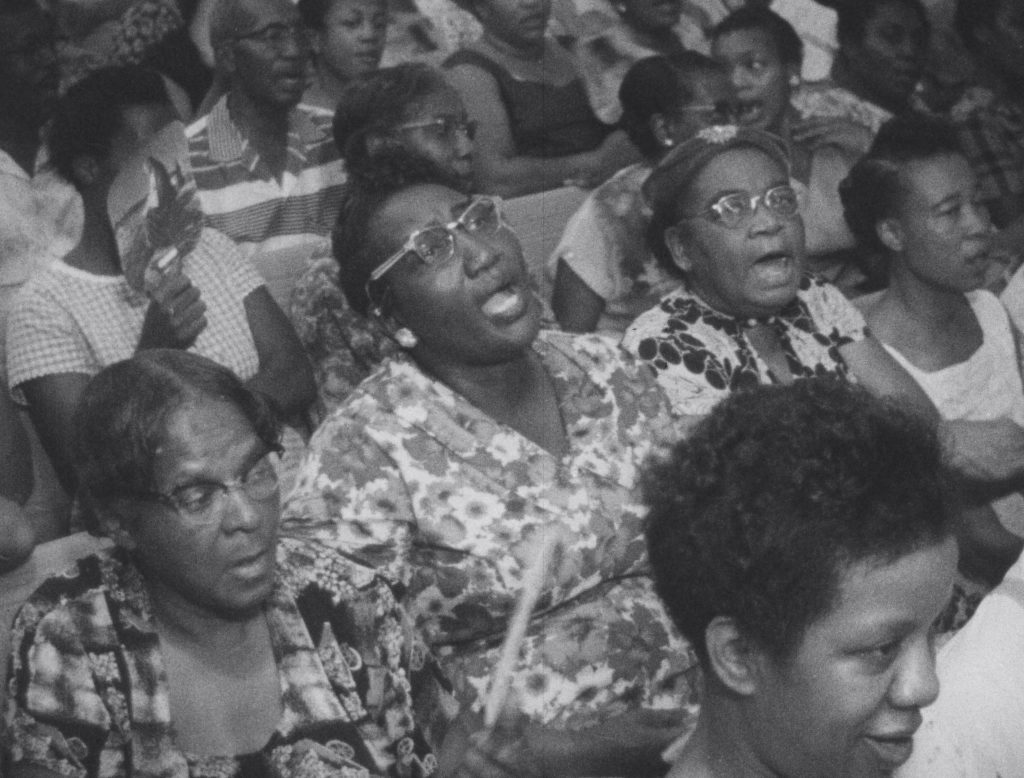

WSB-TV newsfilm clip of an unidentified white female civil rights worker describing the challenges she faces in rural southwest Georgia from Mt. Zion Baptist Church in Albany, Georgia, 1962 August 1. This still image includes participants of a mass meeting, possibly at Shiloh Baptist Church, singing the freedom song, “Keep Your Eyes on the Prize.” Courtesy of the Walter J. Brown Media Archives and Peabody Awards Collection.
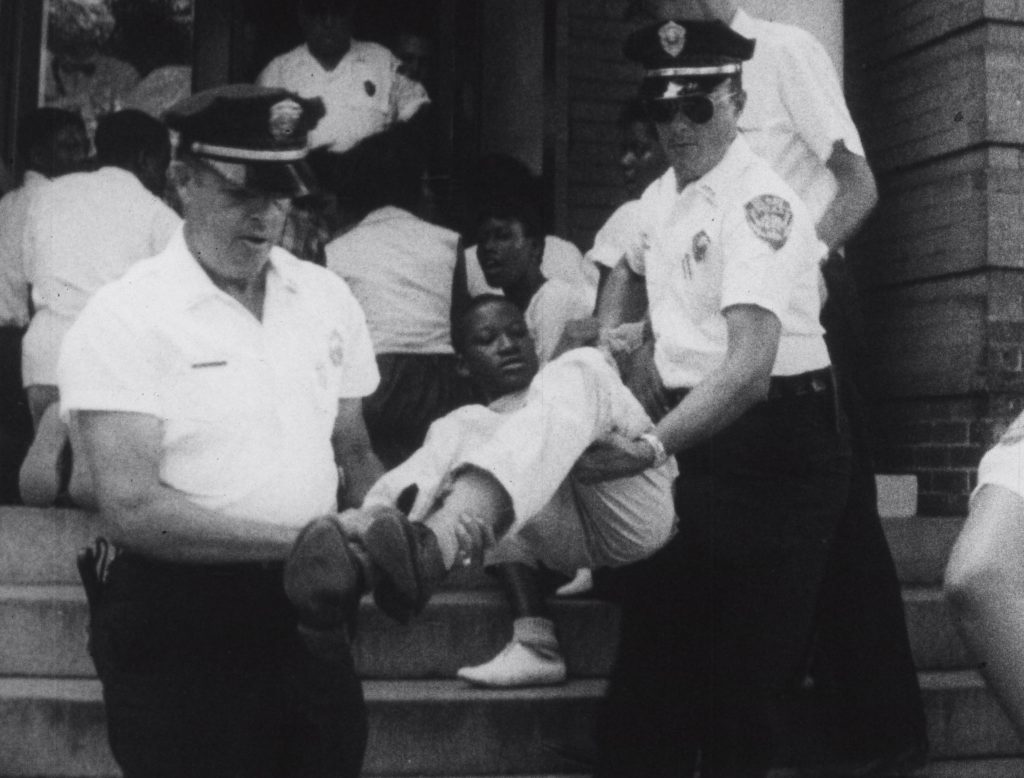

WSB-TV newsfilm clip of African American student protesters singing as they are arrested by police at the Albany Carnegie Library in Albany, Georgia, 1962 August 2. Courtesy of the Walter J. Brown Media Archives and Peabody Awards Collection.