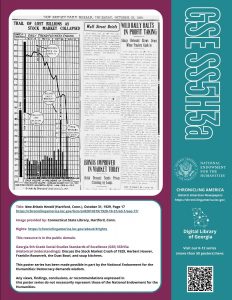
New poster for Georgia K-12 GSE social studies standard SS5H3a
Get the latest printable poster in a series designed for the Georgia K-12 community by the Digital Library of Georgia, based upon the Georgia Social Studies Standards of Excellence.
These resources provide high-quality, standards-aligned materials that help teachers meet their students’ varying academic interests and needs.
The latest poster is for the Georgia 5th Grade Social Studies Standards of Excellence (GSE) SS5H3a (Historical Understandings):
Discuss the Stock Market Crash of 1929, Herbert Hoover, Franklin Roosevelt, the Dust Bowl, and soup kitchens.
Title: New Britain Herald (Hartford, Conn.), October 31, 1929, Page 17
Image provided by:
Connecticut State Library, Hartford, Conn.
Rights:
https://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/about/#rights
This resource is in the public domain.
You can download the poster here.
The poster has been designed to fit an 8.5” x 11” letter-sized sheet of paper, and all content is in the public domain to ensure print accessibility for all students and educators.
Heads up, Georgia K-12 social studies teachers!
Visit us at https://bit.ly/DLGEducatorResources, where you can find:
- Our entire K-12 poster series
- Georgia Standards of Education-aligned Social Studies teaching modules for 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 8th graders
- Resources for teachers and students participating in National History Day and National History Day Georgia.


