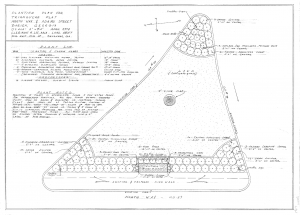
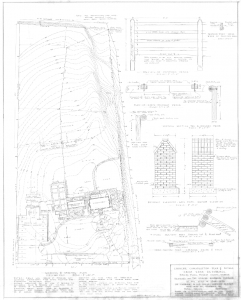
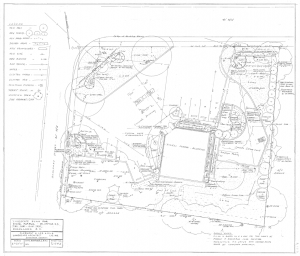
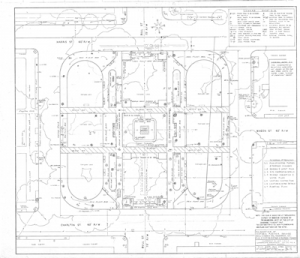
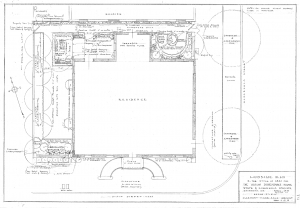
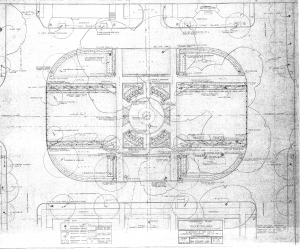
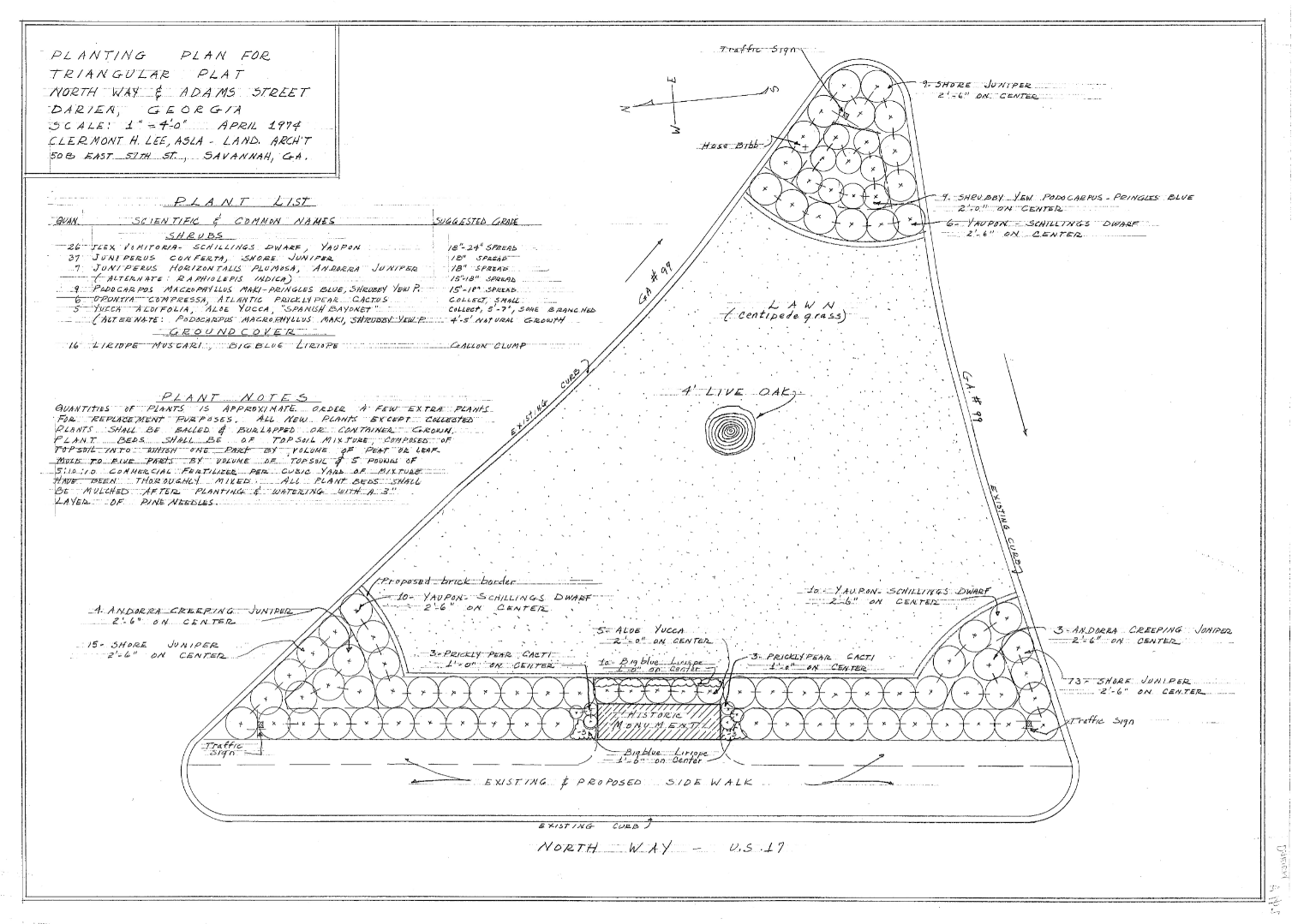
Drawings by Georgia’s first female landscape architect Clermont Lee are now publicly available online thanks to a collaboration between the Georgia Historical Society and the Digital Library of Georgia.
From 1940 through the mid-1980s, she made landscape designs for clients in Savannah, Georgia, and throughout the Southeast.
“These designs provide insight into the less-well documented elements of preservation and restoration projects throughout the state,” notes G. Andrew Fleming, the Friends of Georgia State Parks & Historic Sites executive director.
“Clermont Lee was a pioneering figure in the history of landscape architecture,” says Nate Pedersen, Manager of the Archival and Reference Team at the Georgia Historical Society. “We expect her drawings to be of significant interest to historic preservationists, landscape architects, gardeners, and scholars around the country. As such, we are delighted to be able to freely share her drawings online and are grateful for the support from the Digital Library of Georgia.”
Plans for many Georgia and South Carolina residences, churches, schools, city blocks, office buildings, parks, airports, and historic sites are among the detailed design drawings now available at GHS. Lee is probably best-known locally for her mid-to-late twentieth-century work designing formal gardens for several of Savannah’s historic house museums, including the Owens-Thomas House and the Green-Meldrim House, as well as plans for several of the Landmark District’s beloved squares. Across the state, Lee’s designs include plans for the Chief Vann House in Murray County and Baptist Village in Waycross.
Fleming also adds: “These types of records are invaluable in helping establish a complete picture of our state’s historic spaces.”
About Clermont Lee
Clermont Huger Lee, born in Savannah in 1914, was the city’s first female architect in private practice. She worked as an assistant to T.M. Baumgardner of the Sea Island Corporation during the Great Depression. She became interested in historic gardens in the 1940s after receiving her education at Barnard and Smith Colleges.
As one of the first professional female landscape architects in Georgia, Lee worked with and independently of some of her era’s leading preservationists. She focused on preserving, recreating, and reinterpreting historic gardens and landscapes. This was an aspect of the preservation movement that she felt was ignored in many plans that focused on historic structures.
Lee represents a less recognized part of the movement’s story as both a professional woman working in the field and as a preservationist focused on the natural environment. Historic preservation, particularly during the mid-twentieth century, was associated primarily with professional male architects and developers. Women (usually wealthy white women) worked as volunteers and activists.
In addition to her work in Savannah, she worked on projects throughout Georgia and in cities such as Jacksonville, Florida, and Hilton Head, South Carolina. Lee also worked on the founding of the Georgia State Landscape Architects Board.
Clermont Lee passed away in 2006 on Hilton Head Island, South Carolina.
About the Georgia Historical Society
Georgia Historical Society (GHS) is the premier independent statewide research and educational institution responsible for collecting, examining, and teaching Georgia history. GHS houses the oldest and most distinguished collection of materials related exclusively to Georgia history in the nation. Visit georgiahistory.com/
Selected Images: